Heat Exchanger

Heat Exchanger Parts and Functions:- Heat Exchanger is the most critical and important equipment of any Chemical Plant. It is used to transfer heat from one fluid to another by indirect contact of them. The design of the heat exchanger is very important to increase the efficiency of it. It contains so many different parts that are assembled to produce an efficient heat exchanger. “The heat is always transferred from hot fluid to cold fluid”. Different types of Heat Exchanger are available:
- Shell & Tube HE
- Plate Type HE
- Double Pipe HE
- U-Tube HE
- Fixed Tube HE
- Floating Tube HE
- Air Cooled HE, etc…
In this article, we will discuss some major parts of Heat Exchanger.
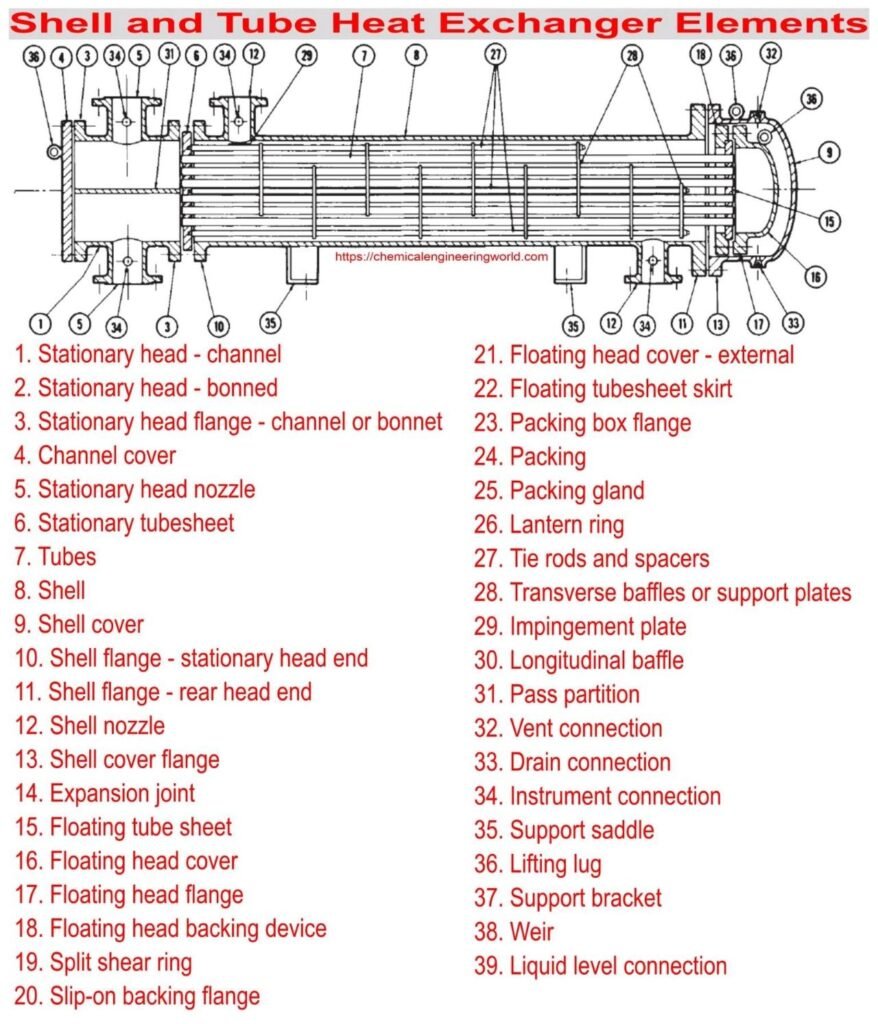
Heat Exchanger Parts
SHELL
SHELL is the component of HE which keeps everything inside it. It is designed based on internal pressure. It has a diameter greater than Tubesheet Diameter. It is closed by head on both sides either flanged or welded. It is made up of metal.
TUBES
TUBES are the second component that carries either hot or cold fluid. Based on the requirement the total number of tubes is decided. Different standard sizes of the tube are available in the market. MOC is selected based on shell and tube sheet material to eliminate galvanic corrosion.
The hot fluid is mostly kept on the tube side to use its heat completely and eliminate heat waste.
Two types of tube pitch are available one is Square which is used when the material is very corrosive and another is Triangular which is used when the material is clear.
TUBESHEET
TUBESHEET is located on both sides of HE. Tubes are fastened on that. IN fixed tube HE TUBESHEET is fixed and cannot be removed and in Floating tube HE It is removable for cleaning purposes.
BAFFLES
BAFFLES are used in the heat exchanger to increase the turbulence of shell-side fluid that increases the heat transfer coefficient. It also gives support to tubes and keeps them in their position. Different types of baffles arrangements are available.
- Segmental Baffles (Most popular)
- Orifice Baffles
- Disc and Donut type baffles
Baffle spacing which is nothing but the distance between two baffles is to be determined very carefully because it directly affects the heat transfer coefficient and pressure drop.
The standard baffle cut is 15% to 40%.
TIE ROD
TIE ROD is the same as the tube which is used to keep spacers on it.
SPACERS
SPACERS are fixed on tie rod to keep baffles in their position and avoid vibration.
NOZZLES
NOZZLES are given for both the fluids shell-side and tube-side. Two for inlet and two for an outlet.
EXPANSION JOINT
EXPANSION JOINT is most useful when the high-temperature variation is given to HE. It will eliminate the expansion and contraction of the heat exchanger which will eliminate cracking of the shell.
PASS PARTITION PLATE
PASS PARTITION PLATE is located on the head which will show the path to fluid in more than 1 pass heat exchangers.
المبادلات الحرارية غلاف وأنبوب – أنا مهندس كيميائي (i-chemeng.com)


